Aquatic Dance: The Art of Synchronized Swimming
Beneath the shimmering surface of water, a group of athletes move in perfect harmony, their bodies twisting and turning with grace and precision. This is synchronized swimming, a captivating blend of dance, gymnastics, and aquatics that challenges both body and mind. Often misunderstood and underappreciated, this Olympic sport demands exceptional strength, flexibility, and artistic expression. Join us as we dive into the fascinating world of synchronized swimming, exploring its rich history, technical intricacies, and the athletes who dedicate their lives to this unique aquatic art form.
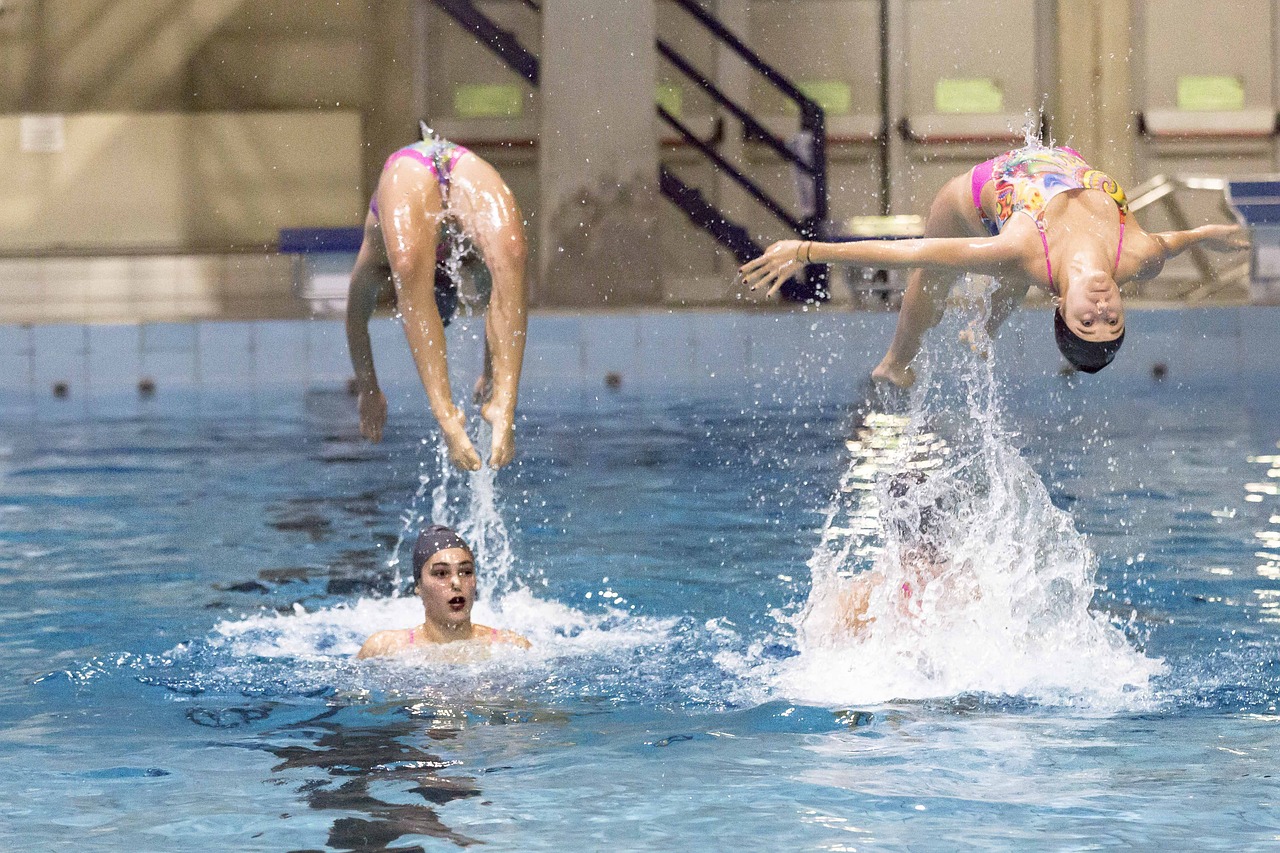
The transition from water ballet to a competitive sport began in the 1930s, largely due to the efforts of Katherine Curtis, an American swim coach. Curtis organized the first synchronized swimming competition in 1939, which helped establish the sport’s fundamental rules and judging criteria. During this period, synchronized swimming gained popularity in aquatic clubs and universities across the United States.
In the 1940s and 1950s, synchronized swimming continued to evolve, with the formation of national organizations and the development of standardized routines. The sport’s international recognition grew, leading to its inclusion as a demonstration event at the 1952 Helsinki Olympics. However, it wasn’t until 1984 that synchronized swimming officially became an Olympic sport, debuting at the Los Angeles Games with solo and duet events.
Today, synchronized swimming is practiced in over 100 countries and continues to push the boundaries of aquatic athleticism and artistry. The sport has undergone significant changes in recent years, including a name change to “artistic swimming” by FINA (Fédération Internationale de Natation) in 2017 to better reflect its athletic nature and appeal to a broader audience.
The Technical Demands of Synchronized Swimming
Synchronized swimming is a sport that demands an extraordinary combination of physical and mental skills. Athletes must possess exceptional strength, flexibility, and endurance while maintaining perfect synchronization with their teammates and the music. The technical aspects of synchronized swimming are complex and multifaceted, requiring years of dedicated training to master.
One of the most challenging aspects of synchronized swimming is breath control. Athletes must perform intricate routines while holding their breath for extended periods, often up to a minute at a time. This requires not only exceptional lung capacity but also the ability to manage oxygen efficiently and remain calm under physical stress.
Spatial awareness is another crucial skill for synchronized swimmers. While performing underwater, athletes must maintain their orientation and position relative to their teammates and the pool boundaries. This is particularly challenging given the disorienting nature of being submerged and the limited visibility in the water.
The sport also demands incredible core strength and body control. Swimmers must be able to perform precise movements and maintain stable positions in the water, often while supporting their entire body weight above the surface. This requires a unique combination of strength, balance, and proprioception.
Flexibility is equally important in synchronized swimming. Athletes must be able to contort their bodies into various shapes and positions, both above and below the water. This requires extensive stretching and conditioning to achieve the level of flexibility necessary for high-level competition.
Choreography and Artistic Expression
While the physical demands of synchronized swimming are undeniable, the artistic elements of the sport are equally important. Choreography plays a crucial role in synchronized swimming routines, blending athletic skill with creative expression to tell a story or evoke an emotion.
Routines are carefully crafted to showcase the athletes’ strengths and interpret the chosen music. Choreographers must consider not only the movements performed above water but also the intricate patterns and formations created beneath the surface. The challenge lies in creating a seamless flow between underwater and above-water elements, ensuring that the routine appears cohesive and captivating from all angles.
Music selection is a critical component of synchronized swimming choreography. The chosen piece must complement the routine’s theme and provide a suitable rhythm and tempo for the athletes’ movements. In recent years, there has been a trend towards more diverse and contemporary music choices, reflecting the sport’s evolution and efforts to appeal to younger audiences.
The artistic aspect of synchronized swimming extends beyond choreography to include costume design and makeup. These elements contribute to the overall visual impact of the performance and help convey the routine’s theme or story. Costumes must be both aesthetically pleasing and functional, allowing for unrestricted movement in the water while remaining secure throughout the performance.
Judges evaluate synchronized swimming routines based on both technical merit and artistic impression. This dual focus ensures that athletes are rewarded for their physical prowess as well as their ability to captivate and engage the audience through their performance.
Training and Preparation
The path to becoming an elite synchronized swimmer is arduous and requires unwavering dedication. Training regimens are intense and multifaceted, encompassing both in-water and dry-land exercises to develop the diverse skill set required for the sport.
A typical training day for a high-level synchronized swimmer can last up to eight hours, with much of that time spent in the pool. In-water training focuses on perfecting technical elements, improving synchronization, and building endurance. Athletes may spend hours repeating specific movements or sequences to achieve the level of precision required for competition.
Dry-land training is equally important and includes a variety of exercises designed to enhance strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular fitness. Strength training is crucial for developing the core and leg muscles needed to perform powerful movements in the water. Flexibility exercises, including yoga and stretching routines, help athletes achieve and maintain the range of motion necessary for intricate poses and positions.
Mental preparation is also a key component of synchronized swimming training. Athletes must develop strong focus and concentration to perform complex routines under pressure. Visualization techniques are often employed to help swimmers memorize choreography and improve their spatial awareness in the water.
Nutrition plays a vital role in the preparation of synchronized swimmers. The sport’s demanding nature requires a carefully balanced diet to fuel long training sessions and support recovery. Athletes must maintain a lean physique while ensuring they have enough energy to perform at their peak.
Team cohesion is essential in synchronized swimming, particularly for group routines. Many teams live and train together year-round to develop the close bonds and understanding necessary for seamless synchronization. This intense shared experience often leads to strong friendships and a unique team culture within the sport.
Competitions and Scoring
Synchronized swimming competitions are structured around several event categories, including solo, duet, mixed duet, and team routines. Each category has its own set of challenges and requirements, showcasing different aspects of the sport’s athleticism and artistry.
International competitions typically feature two types of routines: technical and free. Technical routines require athletes to perform a set of predetermined elements in a specific order, testing their ability to execute precise movements with perfect form. Free routines, on the other hand, allow for more creative expression and are choreographed to highlight the strengths of the individual or team.
Scoring in synchronized swimming is complex and considers multiple factors. Judges evaluate routines based on three main criteria: execution, artistic impression, and difficulty. Execution focuses on the technical aspects of the performance, including synchronization, height of figures, and precision of movements. Artistic impression considers the choreography, musicality, and overall impact of the routine. Difficulty assesses the complexity of the chosen elements and transitions.
The scoring system has evolved over the years to become more objective and transparent. In recent competitions, a panel of technical controllers uses underwater cameras to assess the execution of required elements, ensuring greater accuracy in scoring.
Penalties can be incurred for various infractions, such as touching the bottom of the pool, going over or under the time limit, or performing illegal movements. These deductions can significantly impact the final score, adding an extra layer of pressure to the athletes’ performances.
The Global Landscape of Synchronized Swimming
Synchronized swimming has a diverse global landscape, with strong traditions in various regions around the world. Russia has long been a dominant force in the sport, producing numerous Olympic and World Championship medalists. The Russian school of synchronized swimming is known for its emphasis on technical precision and innovative choreography.
Other countries with strong synchronized swimming programs include China, Japan, and Spain. Each nation brings its own unique style and approach to the sport, contributing to its ongoing evolution and global appeal.
In recent years, there has been a push to increase male participation in synchronized swimming. The introduction of mixed duet events in international competitions has been a significant step towards gender inclusivity in the sport. This development has opened up new possibilities for choreography and has helped challenge traditional perceptions of synchronized swimming as a female-only discipline.
The sport continues to grow in popularity in many developing countries, with national federations working to establish grassroots programs and develop coaching expertise. This global expansion is helping to diversify the talent pool and bring fresh perspectives to the sport.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its beauty and athleticism, synchronized swimming faces several challenges as it looks to the future. One of the primary concerns is increasing public awareness and appreciation for the sport. Many people still view synchronized swimming as a novelty rather than a serious athletic pursuit, which can impact funding, media coverage, and athlete recruitment.
Efforts are being made to address this issue through increased promotion and education about the sport’s physical demands and artistic merits. Some federations are exploring ways to make competitions more spectator-friendly, such as incorporating new technologies to provide underwater views of performances.
Another challenge facing synchronized swimming is the need to continually innovate and evolve to maintain relevance in the modern sports landscape. This includes exploring new event formats, updating judging criteria, and embracing digital technologies to enhance training and performance analysis.
The environmental impact of the sport is also a growing concern. The chemicals used to maintain pool water quality can have negative effects on athletes’ health and the environment. Some organizations are exploring more sustainable pool maintenance practices and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional chlorine-based systems.
Looking ahead, the future of synchronized swimming appears bright. The sport continues to push the boundaries of human performance in the water, blending athleticism and artistry in unique and captivating ways. As it evolves, synchronized swimming has the potential to inspire a new generation of athletes and capture the imagination of audiences around the world.
The Impact of Synchronized Swimming on Athletes’ Lives
Participating in synchronized swimming at a high level has a profound impact on athletes’ lives, extending far beyond the pool. The sport instills a strong work ethic, discipline, and time management skills that serve athletes well in their personal and professional lives.
Many synchronized swimmers report that the sport has helped them develop a deep sense of body awareness and control. This heightened physical intelligence often translates to success in other athletic pursuits and can contribute to overall health and well-being throughout life.
The team aspect of synchronized swimming fosters strong social bonds and teaches valuable lessons in cooperation and communication. Athletes learn to work closely with others towards a common goal, developing interpersonal skills that are highly valued in many professional settings.
The artistic elements of synchronized swimming encourage creativity and self-expression, allowing athletes to develop their artistic sensibilities alongside their athletic abilities. This holistic approach to sport can lead to a lifelong appreciation for the arts and a unique perspective on the intersection of athleticism and creativity.
However, the intense nature of synchronized swimming can also present challenges. The demanding training schedule and physical requirements of the sport can make it difficult for athletes to balance their athletic pursuits with academic or professional commitments. Additionally, the focus on maintaining a specific body type for performance can sometimes lead to issues with body image and self-esteem.
Many synchronized swimmers find that the skills and experiences gained through their sport prepare them well for careers in fields such as coaching, sports administration, performance arts, and fitness instruction. The unique combination of physical discipline, artistic expression, and teamwork cultivated in synchronized swimming can be a valuable asset in a wide range of professional contexts.
Technological Advancements in Synchronized Swimming
As with many sports, technology is playing an increasingly important role in synchronized swimming. From training tools to performance analysis, technological advancements are helping athletes and coaches push the boundaries of what’s possible in the water.
Underwater cameras and motion tracking systems are now commonly used to analyze athletes’ movements and synchronization. These tools allow coaches to provide detailed feedback on technique and timing, helping swimmers make minute adjustments to improve their performance.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies are being explored as training aids for synchronized swimmers. These immersive technologies can help athletes visualize routines, practice spatial awareness, and even simulate competition environments, providing valuable mental preparation opportunities.
Wearable technology is also making its way into synchronized swimming. Waterproof heart rate monitors and accelerometers can provide real-time data on athletes’ physiological responses and movement patterns during training and competition. This information can be used to optimize training programs and monitor fatigue levels to prevent overtraining and injury.
Advances in fabric technology have led to the development of more hydrodynamic and durable swimwear for synchronized swimmers. These high-tech suits can help reduce drag in the water and maintain their appearance even after prolonged exposure to chlorine.
Sound systems used in competitions have also seen significant improvements. Underwater speakers now provide clearer audio for athletes during their routines, ensuring better synchronization with the music and enhancing the overall performance quality.
As technology continues to advance, it’s likely that we’ll see even more innovations in synchronized swimming. From AI-assisted choreography to advanced biomechanical analysis tools, these developments have the potential to further elevate the sport and push the boundaries of human performance in the water.
Conclusion
Synchronized swimming stands as a testament to the incredible capabilities of the human body and the power of artistic expression in sport. This unique discipline challenges athletes to push the limits of strength, flexibility, and endurance while maintaining perfect synchronization and grace under pressure.
From its humble beginnings as a form of aquatic entertainment to its current status as an Olympic sport, synchronized swimming has undergone significant evolution. Today, it continues to captivate audiences with its blend of athleticism and artistry, while also pushing for greater inclusivity and innovation within the sporting world.
As we look to the future, synchronized swimming faces both challenges and opportunities. The sport must continue to adapt and evolve to maintain its relevance and appeal to new generations of athletes and spectators. However, with its unique combination of physical prowess, artistic expression, and teamwork, synchronized swimming is well-positioned to inspire and amaze for years to come.
Whether you’re a seasoned athlete, a curious spectator, or someone looking for a new form of physical and artistic expression, synchronized swimming offers a world of beauty, challenge, and achievement. As this aquatic art form continues to make waves in the world of sport, it invites us all to dive deeper into the fascinating realm where athleticism meets artistry in perfect harmony.




